

Green technology is a challenging field that requires careful consideration for sustainable investors trying to determine which technologies are worth investing in and when is the best time to do so. One tool that can be helpful in this process is the Climate Technology Maturity Curve, also known as the Green Technology Maturity Curve, published by Silicon Valley Bank (SVB). This curve breaks down the life cycle of green technologies from infancy to maturity, including stages such as the innovation trigger, peak expectations, disillusionment, slope of enlightenment, and plateau of productivity.
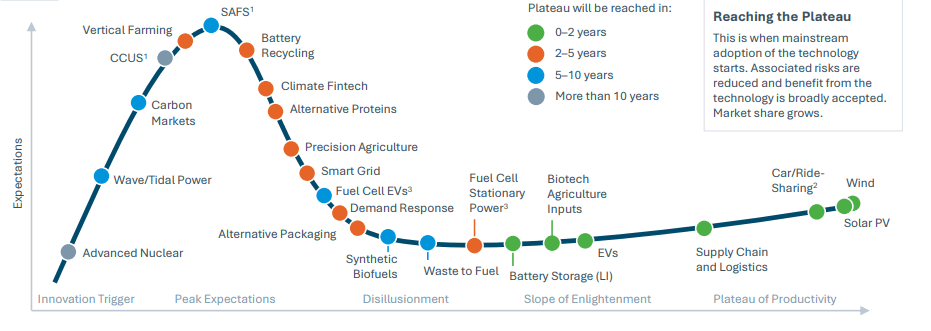
Green Technology Maturity Curve / Source: Future-of-climate-tech-report, Silicon Valley Bank (2022)
The curve can be used to assess the potential for investment in a particular green technology or market entry, as well as to understand which technologies are ready for deployment in carbon neutralization efforts. According to the curve, there are four categories of green technologies based on their development stage and relative position:
Technologies expected to reach the plateau of productivity within 0-2 years: These technologies are expected to be widely adopted in the market, increasing market size and decreasing risk, but also decreasing investment premium. Examples include wind and solar energy, shared transportation, green supply chain and logistics, electric vehicles, agricultural biotech, and battery storage.
Technologies expected to reach the plateau of productivity within 2-5 years: These technologies are also expected to be widely adopted in the foreseeable future and increase market size, but have a higher potential for obtaining an investment premium. Examples include fuel cell stationary power, alternative packaging, demand response, smart grids, precision agriculture, alternative proteins, climate fintech, battery recycling, and vertical farming.
Technologies expected to reach the plateau of productivity within 5-10 years: These technologies are in the early stages of the slope of enlightenment and may require more time and iteration to mature. Examples include advanced nuclear, carbon capture and storage, and advanced materials for energy storage.
Technologies expected to reach the plateau of productivity after 10+ years: These technologies are in the early stages of the innovation trigger and may not yet be well understood or widely recognized. Examples include advanced geothermal, artificial photosynthesis, and advanced biofuels.
By understanding the position of a particular green technology on the maturity curve, investors can make informed decisions about when and how to invest. It is important to note that the curve is not a precise prediction of the future, but rather a tool to help understand the relative position and potential of different technologies.